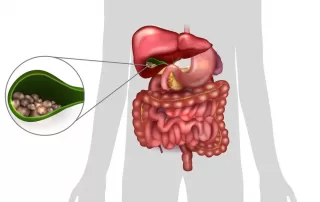
Cholecystitis is the inflammation of the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. This condition is often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct, which leads to a buildup of bile and subsequent inflammation. Other causes can include tumors, bile duct problems, and infections.
Symptoms of cholecystitis include severe pain in the upper right abdomen, especially after eating fatty foods, which may radiate to the right shoulder or back. Other symptoms can include fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness in the abdomen. If left untreated, cholecystitis can lead to serious complications such as gallbladder rupture, infection spreading to other parts of the body, or severe inflammation.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests to check for signs of infection or inflammation, and imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan to view the gallbladder.
Treatment for cholecystitis often involves hospitalisation to manage the symptoms and prevent complications. Initial treatments may include fasting to rest the gallbladder, intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration, and antibiotics to treat any infection. Pain management is also crucial. In many cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is recommended, especially if gallstones are the cause.