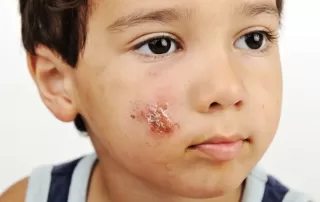
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection commonly affecting children but occasionally adults. It’s caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria and appears as red sores or blisters on the face, hands or feet, which quickly rupture to form a honey-colored crust. It often starts at sites of minor skin injuries such as cuts, insect bites, or areas of eczema.
Prompt treatment is important to prevent the spread of impetigo to others and to reduce the risk of complications. Treatment typically involves antibiotic creams or, in more severe cases, oral antibiotics. To prevent impetigo, good hygiene practices are crucial, including regular hand washing, keeping nails short, and avoiding sharing personal items like towels and clothing.
During treatment, it’s important to keep the affected areas clean, and to ensure children stay home from school or daycare until they’re no longer contagious.