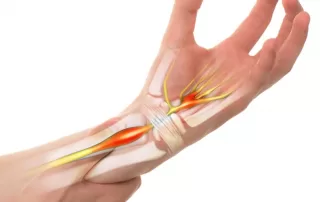
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition in Australia, characterized by numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and lower arm. The syndrome arises from pressure on the median nerve within the narrow carpal tunnel of the wrist, a space that also houses tendons that move the fingers. This pressure can be due to various factors, including repetitive hand movements, wrist injuries, or underlying health conditions that cause swelling. CTS is particularly common among people who perform repetitive manual tasks or use vibrating tools. It has a higher incidence in women, likely due to hormonal factors and smaller carpal tunnels. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to address symptoms and preventing long-term damage, which might include nerve testing and lifestyle adjustments, as well as medical interventions in more severe cases.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-causes, symptoms & treatment
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome- causes, symptoms & treatment what is it? symptoms causes treatment What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a painful condition of one or both hands, caused by pressure on the median nerve The median nerve runs down the arm and into the hand. [...]