Urticaria- what causes hives and how is it treated?
What is Urticaria?
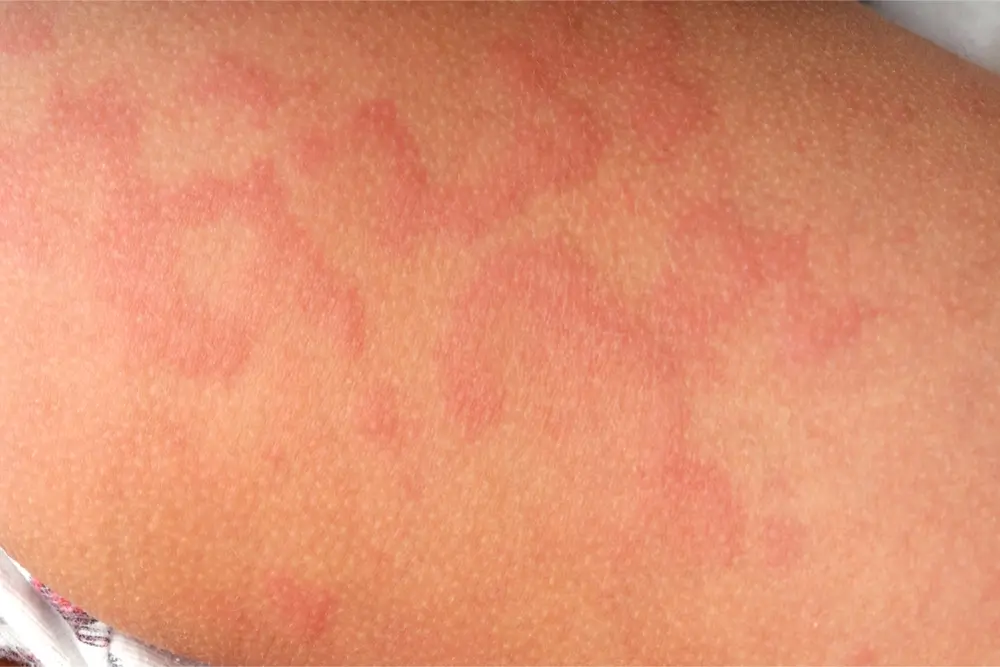
- Urticaria (commonly known as “hives”) is a common itchy rash- around 20% of people get it at some point in life.
- It usually leads to raised pink itchy skin lesions, which can look a bit like mozzie bites.
- These spots can vary in size, from quite small to much larger “welts”- and they can fluctuate quickly- appearing, disappearing and reappearing over minutes hours or days.
- Urticaria is NOT a crusty or blistering rash, and it should always go pale (blanche) when pressure is applied to the lesions.
- An antihistamine may relieve the symptoms.
- If it goes on for more than 6 weeks, it’s considered to be Chronic Urticaria.
What causes Urticaria?
Urticaria (hives) happen when a substance called histamine is released from cells in your skin, leading to swelling and irritation. It’s not known exactly why this happens, but the following may be triggers for urticaria:
- Viral illness- this is a very common trigger in children
- Certain foods
- A side effect of a medicine
- Insect stings or bites
- Exposure to certain plants or animals
- Less commonly it can be caused by physical triggers like cold weather, sunlight, rubbing or pressure on the skin, exercise,
Occasionally, urticaria is part of a more serious allergic reaction – this possibility should be considered if any of the following occur:
- It’s always within 2 hours of a meal
- Tightness of breathing
- Nausea, vomiting and/or tummy pain
- Light-headedness
- Swelling of the throat and/or tongue
If there is breathing difficulty, tongue and mouth swelling, or abdominal pains with the rash it could mean it’s Anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening allergic reaction- immediate medical attention should be sought.
What is the treatment for urticaria?
- If you know the trigger, avoid it.
- Antihistamines may ease the rash and the itch- these are available over the counter from your pharmacist.
- Avoid anything that makes the rash more prominent – like stress, alcohol, getting too hot or hot spicy food.
- It seems anti-inflammatories can make urticaria worse in some people- so these should be avoided. Paracetamol (Panadol) is still OK.
- Sometimes oral steroid medication (cortisone) is prescribed- but it’s often not very helpful, and there are many possible side effects of this treatment.
- People who have chronic urticaria may need to see an allergy specialist or dermatologist for further advice- sometimes they may try medications which act on the immune system.
Are there any tests for urticaria?
- Tests are not usually needed- as they usually don’t offer any helpful information.
- However, if urticaria goes on for more than 6 weeks, or if a person has other unexplained symptoms apart from the rash (eg fevers, pain or feeling generally unwell), blood tests may be advised.
- If there are symptoms suggestive of Anaphylaxis, further allergy testing will usually be recommended.
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide Mental health matters—and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, anxious, or down, a mental health care plan can help. But what is it, and how do [...]
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, uncomfortable, and often disruptive. But what exactly are the signs to watch for, and how can you get relief [...]
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor Discover how to get a free, bulk-billed Mental Health Care Plan (MHCP) in Australia through Qoctor's telehealth service. Accessing [...]





