Syphilis
Medically Reviewed by Dr Aifric Boylan
Last updated on 07.08.2024
As one of the oldest sexually transmitted infections (STI) still present today, syphilis continues to make its mark in the 21st century. In 2023, there were over 8,000 notifications for syphilis in Australia, up from over 2,000 in 2010.
Worldwide in 2022 there were 8 million adults with syphilis and 700,000 babies born with congenital syphilis.
It is an infection that has famously been claimed to have affected Casanova, Oscar Wild, Fyodor Dostoevsky, Ludwig van Beethoven and Vincent Van Gough, while also creating tension between kingdoms and countries in the past.
So, what is syphilis?
It is a bacteria that can be transmitted during sex through the mouth, penis, vagina and anus. It can also be transmitted in blood transfusions, intravenous drug use and pregnancy.
In Australia, there are higher rates of syphilis in gay men and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders.
What are the symptoms?
Unfortunately, this type of STI often has no obvious symptoms and therefore it can easily be missed. If the infection is missed, it can lead to health issues in the future. For example, women can experience miscarriage and in the later stages of syphilis, the bacteria can ravage your body.
There are four stages of syphilis, each with their own symptoms however you can be infectious during each of the stages.
Primary syphilis
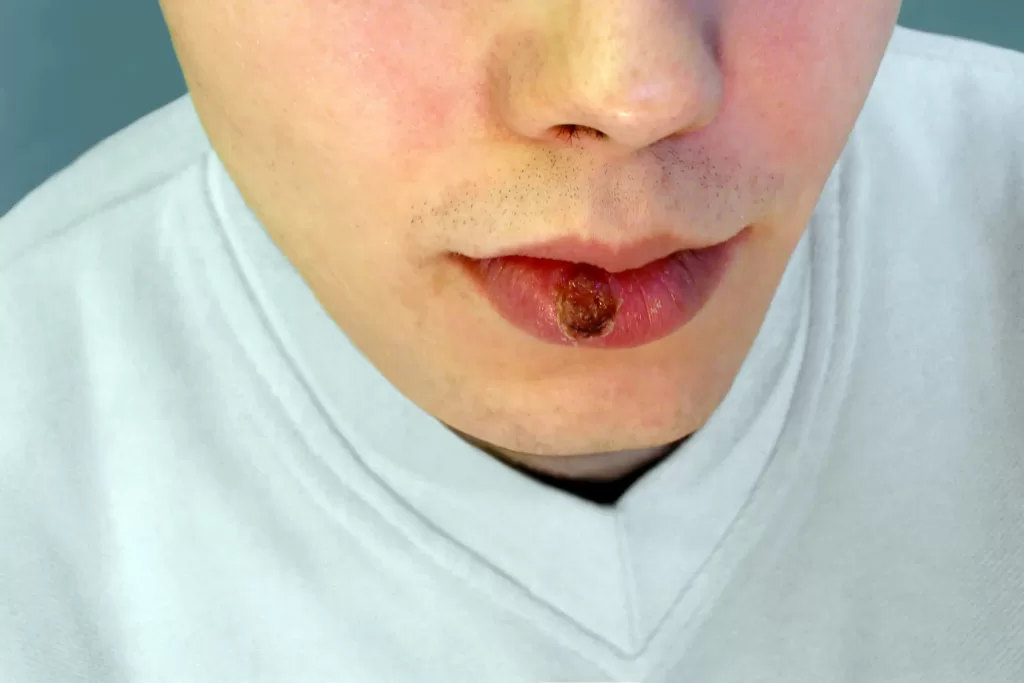
A painless ulcer presents in your mouth, penis, anus or vagina between one week and three months after sex. The ulcer resolves on its own within a month, however you still continue to have the bacteria and can pass it on to others.
Because the ulcer is painless it is easy to miss, particularly if it is inside your mouth, anus or vagina. Therefore, treatment can be delayed if you are not having regular STI screening and you may develop secondary syphilis.
Secondary syphilis
This phase develops 2-3 months after the initial infection and can present with:
- A non-itchy but raised rash on the hands, feet, chest or back
- Fever, fatigue and enlarged lymph nodes
- Hair loss
- Headaches
You continue to be infectious and can transmit the disease to other partners. If you are not treated, you can develop latent syphilis.
Latent syphilis
In this phase, there are usually no symptoms. You continue to remain infectious for up to 2 years after which time the bacteria is less active and less likely to transmit to other partners. Without treatment however, a third of people may develop tertiary syphilis.
Tertiary syphilis
In this phase, which can present many years after the first infection, you can develop blindness, heart disease, mental illness, vertigo, seizures and bone disease. Most people with tertiary syphilis are no longer infectious, however their health is grossly affected by symptoms that can ravage the whole body.
How do you test for syphilis?
There are two tests. If you have primary syphilis and a visible ulcer, your health practitioner can take a swab and confirm the infection.
The other option is a blood test. This is useful in all four stages of syphilis and can also provide an estimation of what stage you are in.
If you have syphilis, you should inform all sexual partners from the previous three months. You can use Let Them Know to discreetly inform partners.
How is it treated?
The best news is that this STI is completely curable with penicillin. This is usually done with an injection into your glutes, however if you are allergic to penicillin there are other options.
Sometimes you can get a fever, muscle aches and malaise a day or so after penicillin treatment. This is a common reaction and is a sign that the bacteria is being eliminated.
You must avoid sex for seven days after treatment and require repeat blood tests 3, 6 and 12 months after treatment to make sure that the infection is cleared and you have not been reinfected.
Prevention
The only way to prevent it is abstinence or condoms. Pregnant women are routinely tested for syphilis in early pregnancy in order to have early treatment.
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide Mental health matters—and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, anxious, or down, a mental health care plan can help. But what is it, and how do [...]
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, uncomfortable, and often disruptive. But what exactly are the signs to watch for, and how can you get relief [...]
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor Discover how to get a free, bulk-billed Mental Health Care Plan (MHCP) in Australia through Qoctor's telehealth service. Accessing [...]